 Ultrasound, also called sonography, is a safe and painless diagnostic medical procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce dynamic visual images of organs, tissues or blood flow inside the body. The high-frequency sound waves are transmitted to the area of interest and the returning echoes are recorded. Sonography can be used to examine many parts of the body, such as the abdomen, breasts, female reproductive system, heart and blood vessels and more.
Ultrasound, also called sonography, is a safe and painless diagnostic medical procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce dynamic visual images of organs, tissues or blood flow inside the body. The high-frequency sound waves are transmitted to the area of interest and the returning echoes are recorded. Sonography can be used to examine many parts of the body, such as the abdomen, breasts, female reproductive system, heart and blood vessels and more.
It is recommended that you wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. You may need to remove all clothing (you will be provided with a gown) and jewelry in the area to be examined.
Pelvic / Renal / Pregnancy Ultrasound
Please drink 32 oz of water 1 hour prior to exam and do not void. Must have a full bladder for these exams.
Renal Artery / Abdomen (RUQ, Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas, and Aorta) Ultrasound
Nothing to eat or drink 6 hours prior to exam.
Abdomen Limited Pyloric Stenosis Ultrasound
Please do not feed the baby 2 hours prior to exam.
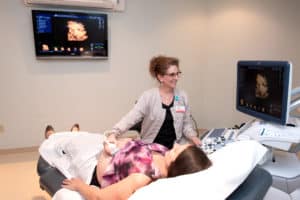
For most ultrasound exams, the patient is positioned lying face-up on a padded examination table which can be tilted or moved. A clear water-based warm gel is applied to the area of the body being studied to help the transducer make secure contact with the body and eliminate air pockets between the transducer and the skin. The sonographer (Ultrasound Technologist) then presses the transducer against the skin and sweeps it over the area of interest.
The sonographer is able to review the ultrasound images in real-time as they are acquired. If you are scheduled for a transvaginal ultrasound, the endovaginal probe is inserted into a woman’s vagina to view the uterus and ovaries.
Most ultrasound examinations are completed within 30 minutes to an hour. Although the ultrasound images are obtained in “real-time”, the technologist will not be able to discuss findings with you during or after the exam as the diagnostic images can be read only by a physician.
